# Prepare your spreadsheet
It's time to turn your spreadsheet into a Relational Database
# A sheet is a table
Okay, it's simpler to have an example, let say we have a sheet like this
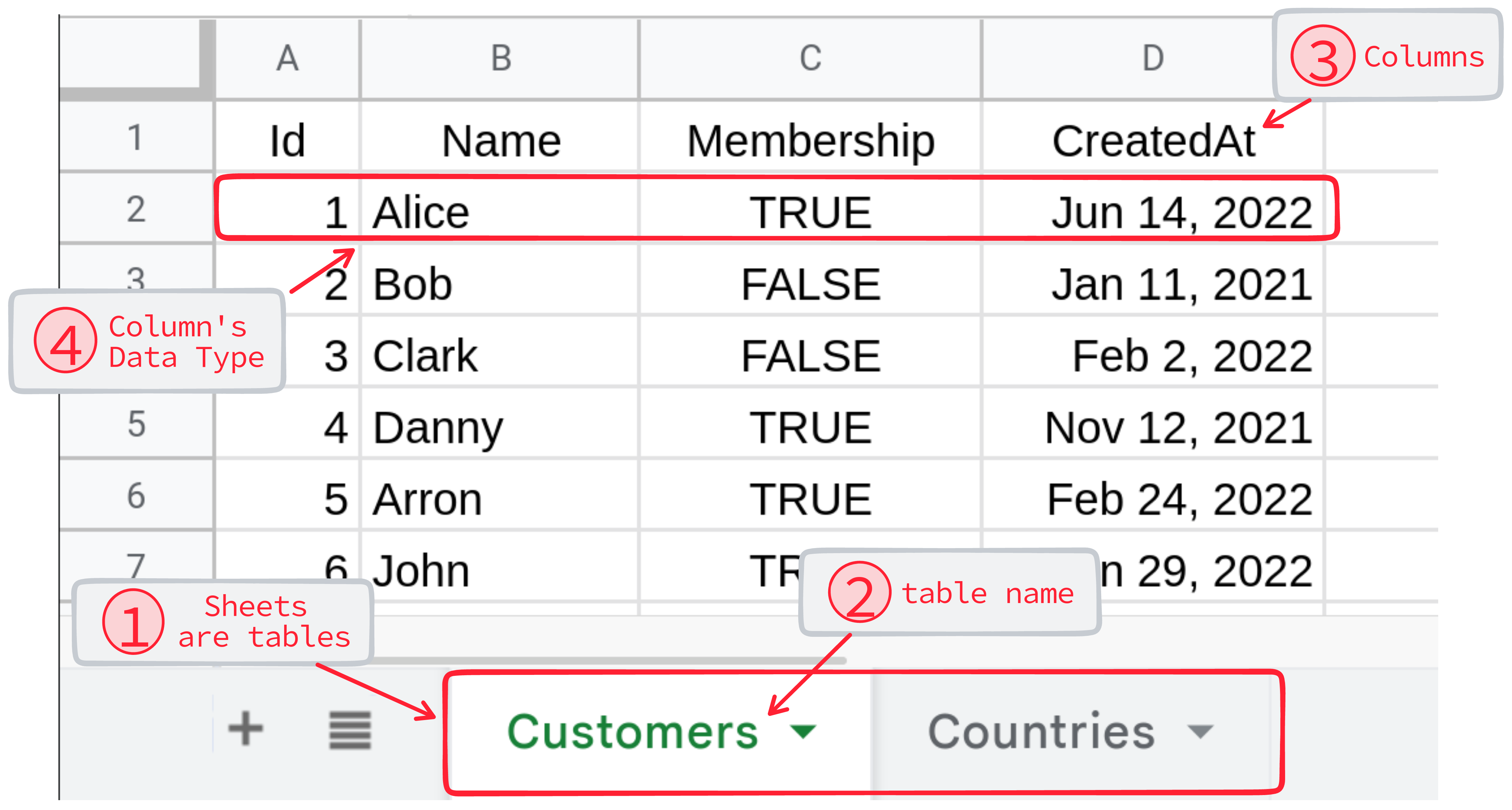
# Essential concepts:
As you can see from above numbers:
- RestSheet treats each sheet in your spreadsheet as a table in a database
- Each sheet's name is mapped to a table name in the database
- The first row of each sheet is treated as the table's header, with each column representing a column in the table
- The data type of each column is determined by the format of the cells in the second row of the sheet
- The remaining rows in the sheet represent data records in the table.
# Instantly turn your spreadsheet into API data
# Sheet names are API endpoints
# JSON API return
After turning your Spreadsheet into API, here is what API result looks like
{
"id": 1
"name":"Alice",
"MemberShip": true,
"CreatedAt": "Jun 14, 2022"
},
{
"id": 2
"name":"Bob",
"MemberShip": false,
"CreatedAt": "Jun 14, 2022"
}
# SQL Support
And here how we will get the data with SQL query
SELECT "id", "name", "MemberShip", "CreatedAt"
FROM "customers"
NOTE
- Sheet name will be normalized, for example, above sheet
Customersis normalized intocustomers - SQL query is PostgreSQL syntax.
- When writing the SQL query, you should wrap the column's name inside a double-quote to get the exact case sensitive column, e.g. above SQL query is querying "MemberShip", "CreatedAt".
← Introduction REST API →